The Asian hornet (Vespa velutina), also known as the yellow-legged hornet, is an invasive species that has rapidly spread across France and other European countries since its accidental introduction in 2004. Originally from Asia, its presence has raised increasing concerns due to its impact on local ecosystems, beekeeping, and biodiversity. This article explores the biology, behavior, ecological impact of the Asian hornet, as well as effective control methods to curb its spread.
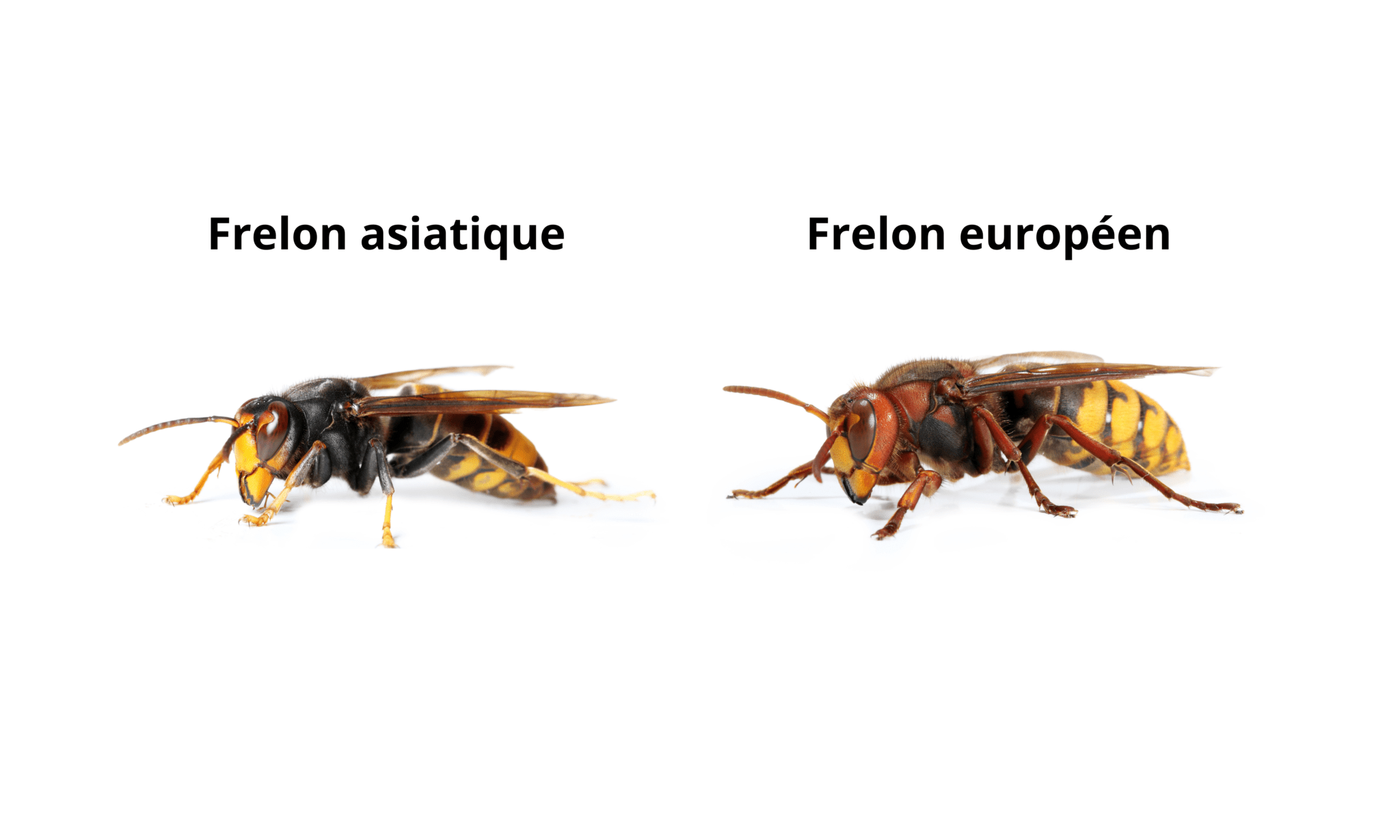
The Asian hornet (Vespa velutina) can easily be confused with other hymenopterans such as the European hornet (Vespa crabro) or certain species of wasps. However, some notable differences allow for precise identification:
Unlike common wasps, which are smaller (1 to 1.5 cm), with a slimmer body and bright yellow and black colors, the Asian hornet is bulkier and darker.
If you are unsure about identification, it is recommended to take a photo and report its presence to local authorities or specialized platforms.

The life cycle of the Asian hornet follows an annual pattern with several key phases:

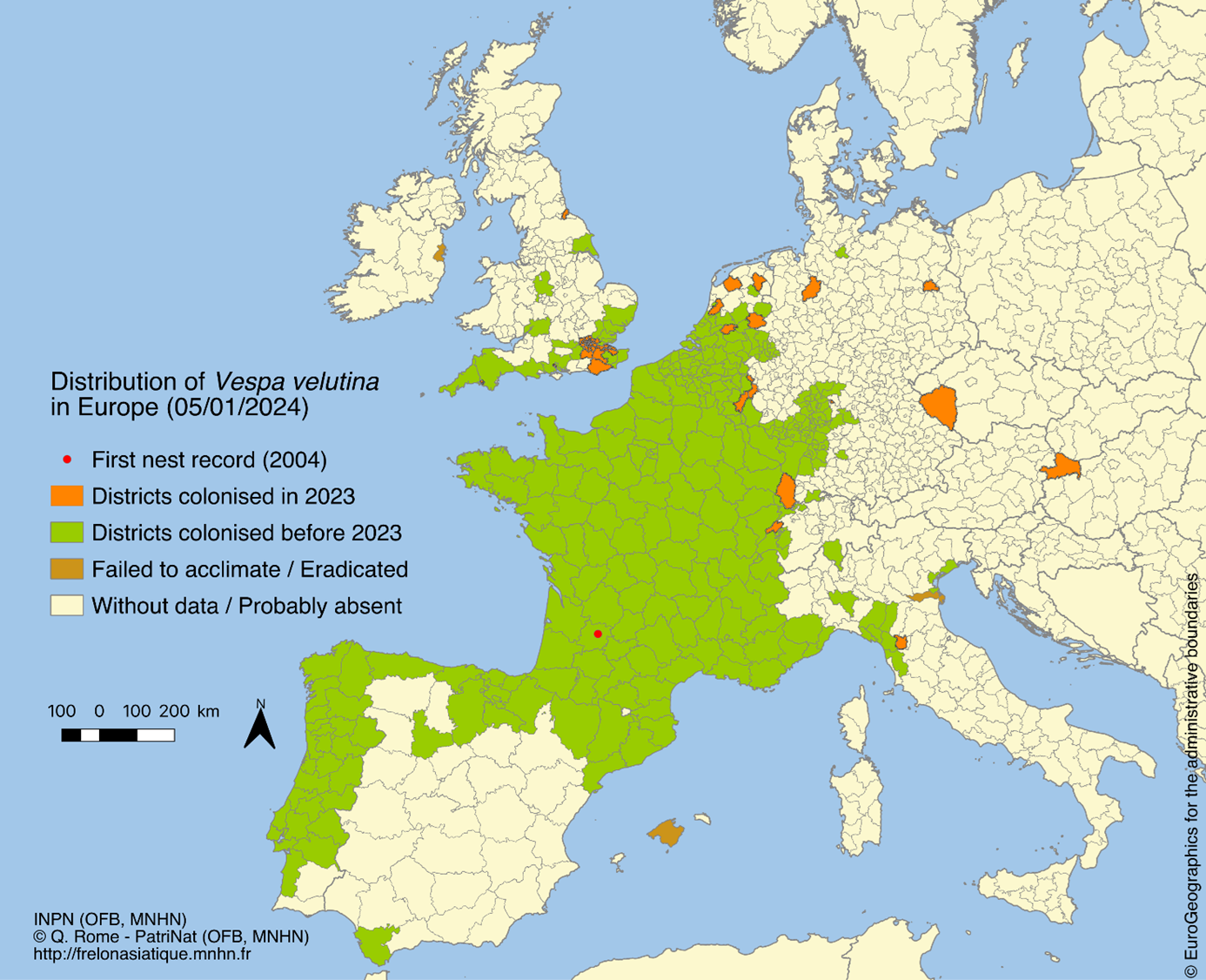
The most probable hypothesis is that the Asian hornet was accidentally introduced into France via the trade of Asian pottery deposited in Lot-et-Garonne. Since then, the species has rapidly spread throughout the country and other European regions. It is now present in most French departments and continues its expansion north and eastward in Europe (Belgium, the Netherlands, Germany, Switzerland…). It prefers urban, peri-urban, and rural areas, building its nests in various locations, from trees to artificial structures.
Since 2016, Vespa velutina has been listed as an invasive alien species of concern by the European Union.
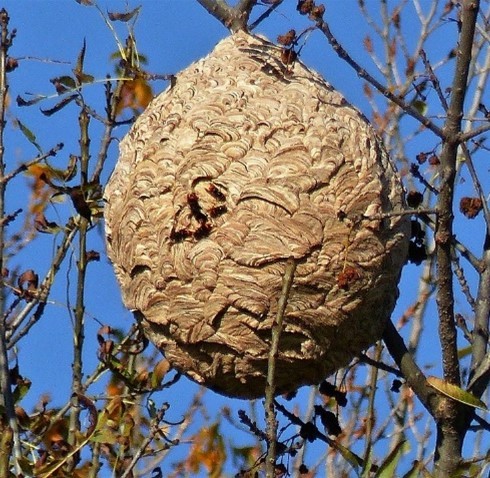
The Asian hornet is a generalist predator that primarily feeds on insects, particularly honeybees, wasps, flies, and butterflies. This intense predation places significant pressure on bee populations, affecting plant pollination and agricultural production.
Moreover, the Asian hornet threatens local biodiversity by reducing pollinator populations and disrupting ecosystems. Its presence can also lead to a decline in honey production and increase stress on bee colonies, jeopardizing their survival.
Control Methods Against the Asian Hornet
Several strategies are employed to manage Asian hornet populations:
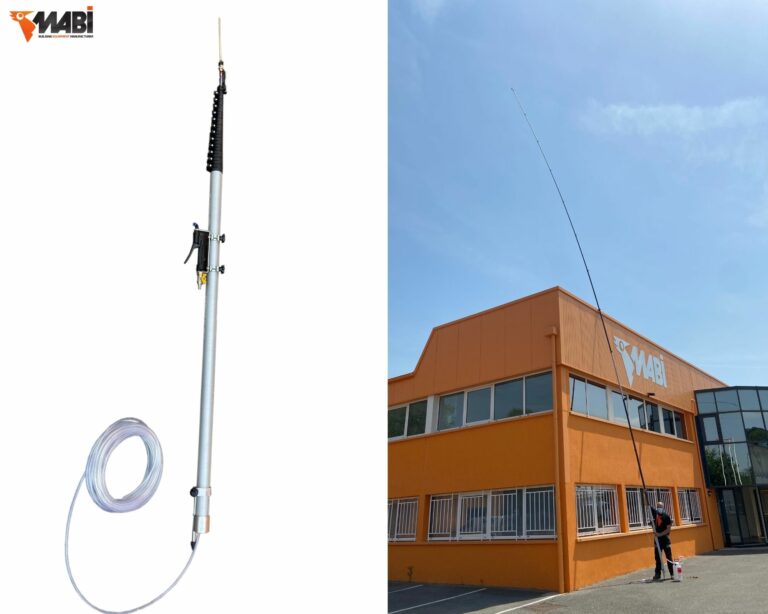
To safely and effectively combat the Asian hornet, appropriate equipment is essential:
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
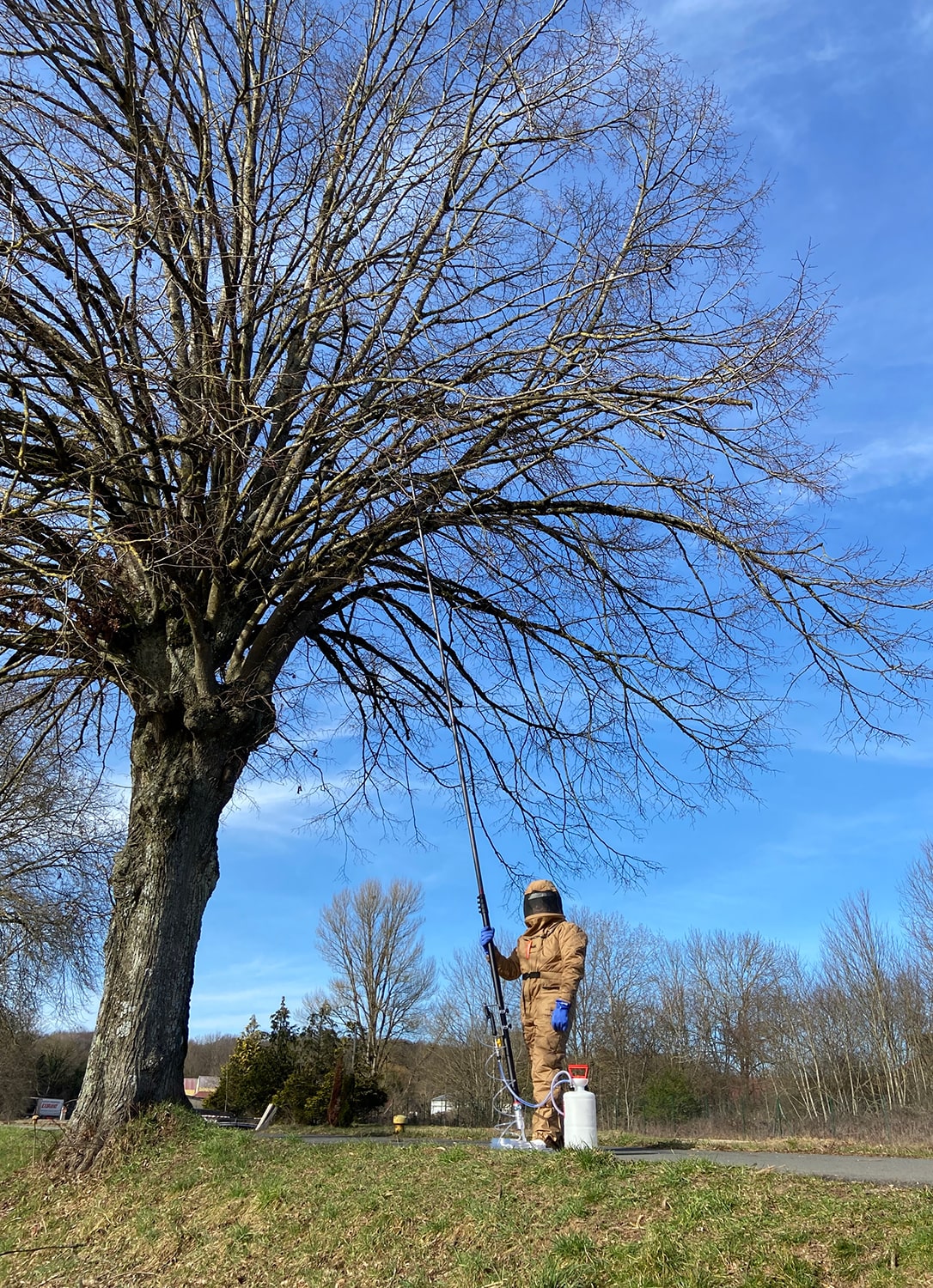


3. Safety Measures During Intervention

Conclusion
The Asian hornet poses a serious threat to biodiversity, beekeeping, and European ecosystems. A thorough understanding of its biology and behavior is essential for developing effective management strategies. Collaboration between researchers, beekeepers, local authorities, and the public is crucial to monitor and control the spread of this invasive species while minimizing